However, its mercury content has raised health concerns, and many people are now choosing to have their amalgam fillings removed in favor of safer, more aesthetic alternatives.
If you're considering this step, it's crucial to understand what amalgam is made of, how it compares to other materials, and how to remove it safely using the SMART protocol.
What Is Amalgam Made Of?
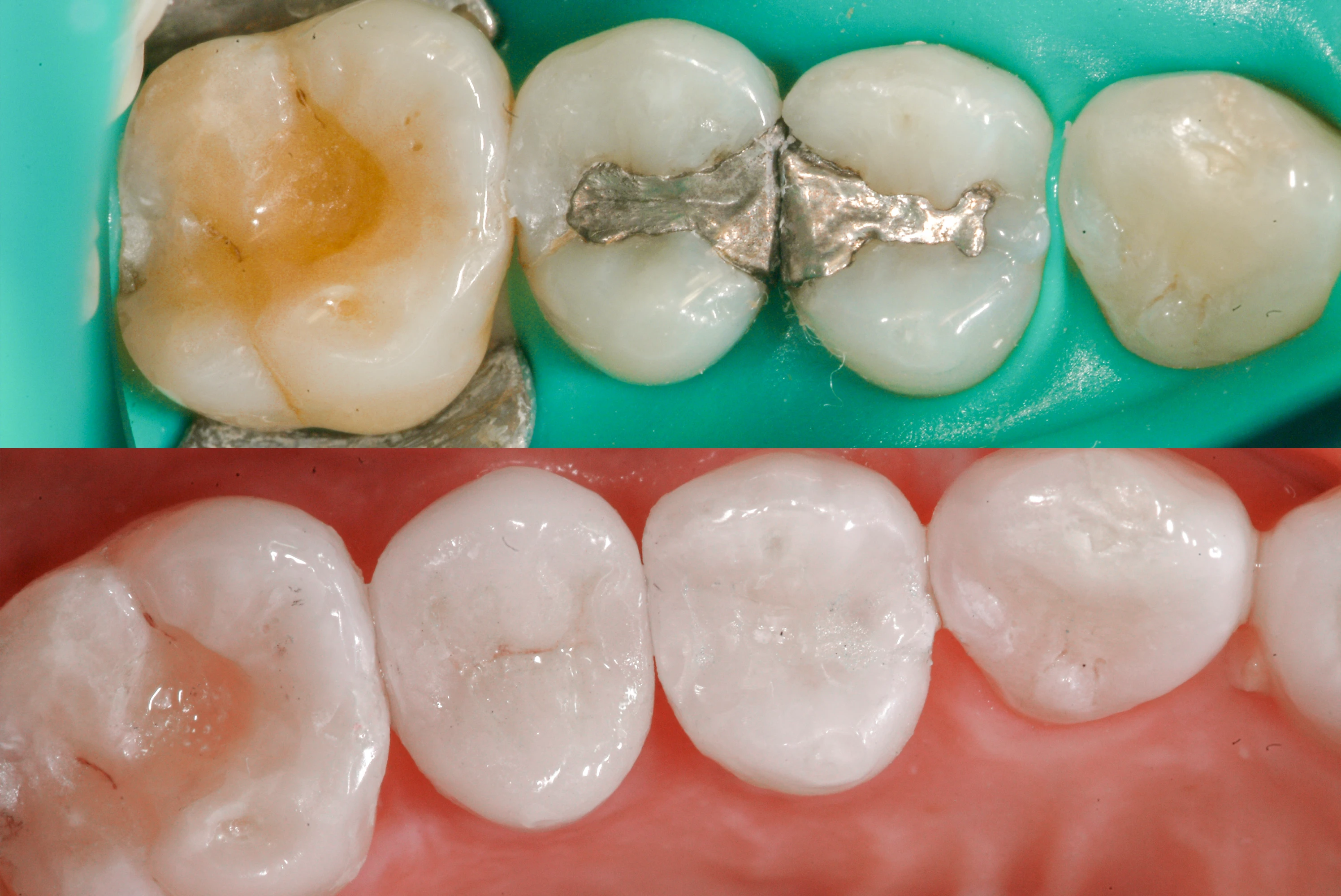
Amalgam material is a mix of approximately 50% elemental mercury and a powdered alloy of silver, copper, tin, and zinc. Mercury is used because it binds these metals into a hard, durable substance that sets quickly, making it ideal for tooth amalgam restorations, especially in the back teeth where chewing force is highest.
While its strength is a plus, amalgam fillings release mercury vapor, especially during chewing, brushing, or when drinking hot beverages. Over time, this vapor can accumulate in the body, leading to potential toxicity, especially for individuals more sensitive to mercury.
Comparing Amalgam vs Composite Resin
One of the biggest debates in dentistry is amalgam vs composite resin. While composite resin fillings are tooth-colored, more aesthetic, and free from mercury, they tend to wear down more quickly and may not last as long in high-pressure areas. However, composite fillings are a safer and more biocompatible alternative for many patients, especially those concerned about amalgam fillings side effects.
So, composite or amalgam?
If durability is your top concern and you have no health issues, amalgam might still seem like a viable option.
But if aesthetics, long-term health, or sensitivity to metals are priorities, composite resin is the better choice.
Mercury Toxicity: What You Should Know
One of the main concerns around amalgam is its mercury content, which can contribute to mercury accumulation in the body, a phenomenon known as bioaccumulation. Over time, mercury can lodge in organs and tissues, including the kidneys and brain.
Common symptoms of mercury poisoning from amalgam fillings or symptoms of mercury toxicity from amalgam fillings include:
Fatigue and brain fog
Memory problems
Mood swings or anxiety
Metallic taste in the mouth
Digestive disturbances
Headaches
While not everyone with amalgam filling teeth experiences these symptoms, individuals with underlying conditions, mercury allergies, or high exposure from other sources (e.g., seafood or certain work environments) may be more vulnerable.
Is Removal the Right Choice?
Many people report positive outcomes after removing amalgam fillings. It's not uncommon to hear someone say, "amalgam removal changed my life", especially those who experienced unexplained health symptoms before removal. However, it's important to proceed with caution.
If your amalgam fillings are intact and there's no decay, immediate removal isn't always necessary. But if you're experiencing health symptoms, have a compromised immune system, or are in a high-risk group (pregnant, nursing, under 15, or with kidney/neurological issues), you might benefit from safe removal.
The SMART Protocol: The Safe Way to Remove Amalgam
SMART stands for Safe Mercury Amalgam Removal Technique, developed by the International Academy of Oral Medicine and Toxicology (IAOMT). It's the gold standard for amalgam filling removal, ensuring minimal mercury exposure for both patients and dental professionals.
Here's what to expect during a SMART amalgam fillings removal procedure:
Rubber dam isolationto protect your airway and soft tissues
High-volume suction with filtration to safely capture mercury vapor and particles
Oxygen supply through a nasal mask to prevent mercury inhalation
Chunk removal technique to minimize drilling and mercury vapor release
Charcoal rinse before and after to help detoxify heavy metals
Protective equipment for the dental team, including mercury-rated masks
Room filtration systems to ensure clean air during the procedure
These steps are critical to reducing the side effects of removing amalgam fillings and ensuring a safe experience. Without these precautions, amalgam extraction can expose patients to a spike in mercury vapor, which may lead to short-term symptoms such as fatigue, dizziness, or nausea.
Are There Side Effects After Removal?
Although many patients report improvements in energy, clarity, and overall well-being after removal of dental amalgam, others may experience temporary symptoms. Removing amalgam fillings side effects can include:
Headaches
Mild fatigue
Mood swings
Digestive upset
These symptoms are usually short-lived and can be minimized with proper detox support, hydration, and rest.
Longevity of Amalgam Fillings
You might wonder: how long do amalgam fillings last? or how long does an amalgam filling last? Generally, silver amalgam fillings can last 10 - 15 years, sometimes even longer with good oral hygiene. However, their aesthetic drawbacks and potential health concerns have encouraged many to transition to newer materials.
 Fatigue and brain fog
Fatigue and brain fog